Jurte/en: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Doro (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
Doro (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| Zeile 8: | Zeile 8: | ||
The most common designs we show you here, hoping this will encourage you to try out your own ideas. | The most common designs we show you here, hoping this will encourage you to try out your own ideas. | ||
A detailed list you can find in the | A detailed list you can find in the [[Stückliste_Jurte|Stücklisten]]. | ||
===Yurt=== | ===Yurt=== | ||
Version vom 6. April 2017, 18:41 Uhr
The yurt is a Mongolian tent form and consists of a sloping roof with vertical side walls.
The basic yurt is built from 6 Kohtenblätter (kota panels, for the roof) and 12 Viereckzeltbahnen (square panels) as side walls. This tent allows 20 people to sit comfortably around a big, cosy campfire.
The yurt can also be connected with other yurts to build bigger constructions. Like combs in a beehive a nearly unlimited number of yurts can be joint together to construct huge tents.
This original yurt can be put up in many ways and if you like to experiment you can vary the way you pitch your yurt. The most common designs we show you here, hoping this will encourage you to try out your own ideas.
A detailed list you can find in the Stücklisten.
Yurt
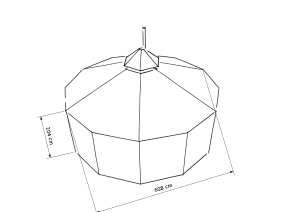
The original size yurt consists of 6 kota panels (for the roof) and 12 square panels (for the side walls). The diameter of this yurt is 6 m, hight of the side walls is 1,60 m and hight of the smoke hole is 2,5 m. The floor space of this yurt is about 29 m² and offers room for about 25 people.
The yurt's roof can be made of a roof tarp (with or without eaves) in one piece, of 2 half roof tarps or of 6 kota panels.
Super-Yurt
The Super-Jurte has higher side walls. Hight of the side walls is 2,09 m and the floor space is also about 29 m². The additional hight provides more options for using the yurt, especially if people inside are standing.
Auch bei der Super-Jurte besteht die Kombinationsmöglichkeit mit Komplettdach, Halbdächern oder einzelnen Kohtenblättern.
Großjurte
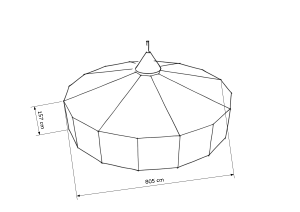
Die Großjurte hat einen Durchmesser von ca. 800 cm, eine Seitenhöhe von ca. 165 cm und eine Mittelhöhe bis zu 300 cm. Die Grundfläche hat ca. 50 m². Damit können in der Großjurte bis zu 50 Menschen unter.
Bei der Großjurte gibt es nur die Möglichkeit ein Komplettdach zu verwenden. Einzelne Kohtenblätter können nicht zu einer Großjurte kombiniert werden.
Super-Großjurte
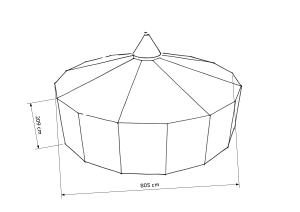
Die Super-Großjurte entspricht der Großjurte mit erhöhten Seitenwänden von ca. 209 cm. Es gilt das gleiche, wie für die Super-Jurte: Durch die höheren Seitenwände können sich mehr Menschen aufrecht im Zelt aufhalten.
Theaterjurte
Die Theaterjurte wird auch Ovaljurte genannt. Sie entsteht durch die Verlängerung einer normalen Jurte oder Super-Jurte um zusätzliche Zwischendachplanen und Seitenwände. Die Theaterjurte könnte theoretisch beliebig verlängert werden. Praktikabel sind meist Ergänzungen um ein, zwei oder drei Segmente. Die Grundfläche der Jurte erhöht sich je Segment um ca. 9 m².
Barbarossa
Das Jurtendach Barbarossa hat eine wesentlich steilere Dachneigung und ein kleineres Rauchloch, als ein herkömmliches Jurtendach. Die geringere Neigung zu Wassersäcken ist nur ein kleiner Vorteil, denn zusammen mit der neuen Trapezplane und einem nachrüstbarer Volant macht dies die alte Jurte damit zu einem vollwertigen Ritterzelt.
Fünfer-Jurte
Die Fünfer-Jurte stellt im Grunde eine Mischform von Kohte und Jurte dar. Sie entsteht durch die Verbindung von fünf Kohtenblättern oder der Verwendung des speziellen Fünfer-Jurtendach mit ca. 500 cm Durchmesser.